If federal student loans don’t fit your needs, compare private student loan interest rates and lenders to find the right financing option for your college expenses.
Table of Contents
Top Lenders For Private Student Loans
| Lender | Learn More | Fixed APR | Variable APR | Max. Loan Amount | Min. Credit Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| View Disclosure | Earnest4.8 | Apply Now | 3.47% to 16.49% with autopay | 4.99% to 16.85% with autopay | Not disclosed | 650 |
| View Disclosure | College Ave4.7 | Apply Now | 3.59% to 17.99% with autopay | 5.34% to 17.99% with autopay | Not disclosed | Mid 600s |
| View Disclosure | Sallie Mae4.6 | Apply Now | 3.49% to 15.49% with autopay | 4.79% to 14.96% with autopay | No maximum | Mid 600s |
| View Disclosure | Nelnet Bank4.6 | Apply Now | 3.69% with autopay to 10.33% | 5.83% with autopay to 10.01% | $500,000 | mid to high 600s |
| View Disclosure | ELFI4.6 | Apply Now | 3.69% to 14.22% | 5.00% to 13.97% | No maximum | 680 |
| View Disclosure | SoFi4.5 | Apply Now | 3.54% to 16.85% with all discounts | 5.54% to 16.85% with all discounts | No maximum | 640 |
| View Disclosure | Ascent Funding4.5 | Apply Now | 3.39% to 14.16% with autopay | 5.25% to 14.26% with autopay | $200,000 | Low to Mid 600s |
| View Disclosure | Citizens4.3 | Apply Now | 3.99% to 15.61% with auto and loyalty discount* | 5.89% to 16.51% with auto and loyalty discount | $350,000 | Not disclosed |
| View Disclosure | PNC4.2 | Read Review | As low as 6.69% with autopay* | As low as 8.44% with autopay* | $50,000 | Not disclosed |
| RISLA4.2 | Read Review | 4.45% to 8.99% | Not disclosed | $50,000 | Not disclosed |
Lenders in More Detail
1 Earnest
View Disclosure
- 4.8
- U.S. News RatingMinimum FICO Credit Score
- 650
Variable APR - 4.99% to 16.85% with autopay
Fixed APR - 3.47% to 16.49% with autopay
Check RatesFrom Our Partner
2 College Ave
View Closure
- 4.7
- U.S. News RatingMinimum FICO Credit Score
- Mid 600s
Variable APR - 5.34% to 17.99% with autopay
Fixed APR - 3.59% to 17.99% with autopay
Check RatesFrom Our Partner
3 Sallie Mae
View Disclosure
- 4.6
- U.S. News RatingMinimum FICO Credit Score
- Mid 600s
Variable APR - 4.79% to 14.96% with autopay
Fixed APR - 3.49% to 15.49% with autopay
4 Nelnet Bank
View Disclosure
- 4.6
- U.S. News RatingMinimum FICO Credit Score
- mid to high 600s
Variable APR - 5.83% with autopay to 10.01%
Fixed APR - 3.69% with autopay to 10.33%
5 ELFI
- View Disclosure
- 4.6
- U.S. News RatingMinimum FICO Credit Score
- 680
Variable APR - 5.00% to 13.97%
Fixed APR - 3.69% to 14.22%
Apply for Federal Financial Aid First
Before you consider private student loans, make the most of federal and free financial aid, including private scholarships.
“Your first step in financing your education is to submit a Free Application for Federal Student Aid, commonly called a FAFSA,” says Jay Fleischman, a lawyer who advises student loan borrowers on effective repayment strategies.
Even if you don’t think you’ll need financial assistance or think you won’t qualify, submit the FAFSA, which is the key to most financial aid. You may be eligible for federal Direct Unsubsidized Loans, but there are limits on how much you can borrow each academic year and overall. Annual borrowing limits range from $5,500 to $20,500.
If you’ve reached the federal student loan borrowing limit and you’ve exhausted other means for paying for college – such as federal PLUS loans, grants and scholarships – then you might consider private student loans to bridge the financing gap.
How Do Private Student Loans Work?
Private student loans are offered by private lenders and banks, whereas federal student loans are funded by the Department of Education. Unlike federal student loans, private student loans do not offer standard repayment plans and interest rates. Your credit, and that of a co-signer if you have one, affect the types of loans available to you and the student loan interest rate you’ll pay.
Loan Types
Private lenders may offer different types of loans depending on the degree you’re pursuing. The loan type can affect your loan amount, interest rate and repayment terms.
- Undergraduate school loans. You can take out undergraduate loans from a private lender to pay for expenses while you pursue a bachelor’s degree.
- Graduate or professional school loans. Graduate school loans tend to have higher maximum loan amounts than undergraduate loans, reflecting the higher cost of attending school for a master’s degree or doctorate. Some lenders feature special loan programs for business, law or medical school.
- Parent loans. Lenders offer these to parents of students. Some families have an informal agreement that the child will make loan payments after graduating, but the legal responsibility to repay the loan falls on the parents.
- Community college or technical training. Some lenders provide loans to students who are pursuing two-year degrees, attending nontraditional schools or completing career-training programs.
Loan Terms
The loan term is the length of the loan’s repayment period, which could range from five to 20 years for private student loans. Typically, shorter loans offer lower interest rates and lower total costs. They’re a good option if you can afford the payments, which tend to be higher. On the other hand, longer-term loans may come with lower payments, but they’re usually more expensive to repay in the long run.
Loan Limits
Lenders may set a maximum annual amount you can borrow or establish a combined private and federal amount you must fall under to qualify for a loan. You may also be limited to borrowing up to your school’s certified cost of attendance, which is outlined in your financial aid award letter.
Most lenders also have minimum amounts you must borrow, which may vary based on your state. Where minimum loan amounts are higher, a private student loan may not be the best option if you only need a few hundred dollars for textbooks or another small expense.
Interest Rate Types
Lenders offer student loans with either fixed or adjustable interest rates. Carefully consider your options because you may not be able to switch your interest rate type after taking out a loan, without refinancing.
When you’re comparing student loans from different lenders, look at the annual percentage rate, or APR, rather than just the advertised interest rate. The APR is your total cost of borrowing each year and includes interest and fees.

Pros and Cons of Private Student Loans
Pros
- Potentially lower interest rates. For well-qualified applicants, private student loans may offer more competitive interest rates than other gap funding options, like Direct PLUS loans. However, private student loan rates can run high for borrowers with bad credit.
- Usually no origination fees. Many private student loan lenders don’t charge origination fees, although they may charge prepayment penalties or late fees. On the other hand, federal student loans have loan fees, which are subtracted from your loan amount and reduce the payout that you ultimately receive.
- Ability to compare rates. Private student loan lenders let you prequalify to check your estimated interest rate and loan terms with a soft credit inquiry, which won’t hurt your credit score. This helps you compare costs and shop around with multiple lenders before formally applying for a loan.
- Co-signer release. Some lenders offer a co-signer release, in which the co-signer is removed from the loan after the student makes a certain number of on-time payments and meets other eligibility criteria.
- Speed. Private student loans are generally processed faster than federal student loans. Some providers advertise that they can deliver approval in hours and funds in days.
Cons
- Credit-based eligibility. Private student loans require a credit check, and their terms depend on the applicant’s credit rating. Without a creditworthy co-signer, many students may not be able to get approved or may only qualify for a high interest rate. Federal student loans (except federal PLUS loans) do not require a credit check.
- No guaranteed hardship options. Private student loans aren’t eligible for federally mandated deferment options, forbearance programs and income-driven repayment plans. Some private student loan lenders offer deferment or forbearance options, but they might not be as flexible as your options with federal student loans.
- No federal forgiveness programs. Several federal student loan forgiveness and cancellation programs aren’t available with private student loans, such as Public Service Loan Forgiveness and borrower defense to repayment.
- Shorter default period and little recourse. Federal student loans go into default status after 270 days of nonpayment, and when they do, you may have several options for getting your loans out of default. Private student loans are typically charged off when they become 120 days past due, according to the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau.
- Risk for co-signers. Co-signers take on debt and risk when they add their names to private student loans, since they will be equally responsible for repaying the debt. If the student can’t make payments on time, this can hurt the co-signer’s credit.
Also Read: Top 14 Business Funding Options For Starting Your Business
Private Student Loan Interest Rate Trends
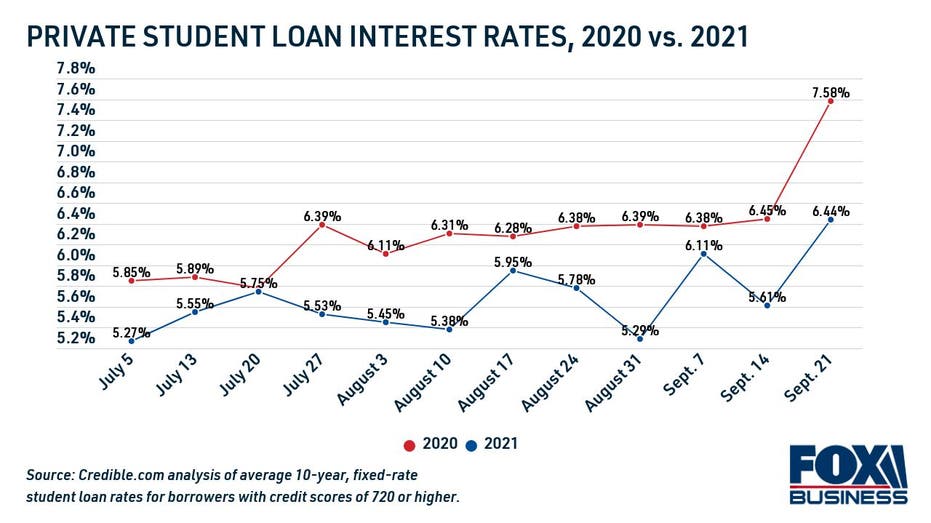
Student loan interest rates stayed about the same last month, according to a U.S. News analysis of minimum and maximum APRs reported by private lenders. Student loan rates have trended higher during the past year, with variable rates climbing by a higher margin than fixed rates.
Here are the in-school student loan rates offered during the month of November 2024:
- Average fixed APR range: 3.82% – 15.35% (Compared to 3.84% – 15.14% the previous month).
- Average variable APR range: 5.54% – 15.73% (Compared to 5.62% – 15.70% the previous month).
The APRs on the lower end of the range are generally reserved for applicants with a high credit score and low debt-to-income ratio, while those with poor credit or limited income will see higher rates.
If you don’t have the credit history needed to qualify for a competitive student loan rate, consider enlisting the help of a co-signer. Additionally, shop around with multiple student loan lenders to ensure you’re getting the lowest possible rate for your financial situation.
Choosing the Best Private Student Loan
Focus on these key areas when comparing private student lenders, according to the Federal Trade Commission, the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, the Department of Education and countless consumer reviews:
- Cost. The cost of your private student loan depends on several factors, including the interest rate and the type of interest. Look closely at fees to calculate how they’ll affect your total cost of borrowing. Always read the loan terms closely to identify potential fees.
- Products. Determine the type of student loan you’ll need, how much you want to borrow, and check that the lenders’ offerings match your requirements. Compare loan terms and limits to narrow your list.
- Eligibility requirements. Research lender eligibility criteria, such as citizenship, enrollment status, age and income and credit history.
- Additional features. The fine print of private student loans can vary from one lender to another. Some features or benefits could make repayment easier, lower your interest rate or help you choose the right lender for your needs.
CALCULATE: Use Our Free Loan Calculator to Estimate Your Monthly Payments.
How to Get a Private Student Loan
The private student loan process is generally faster than that of federal student loans.
- Check your eligibility: The lender will check basic eligibility for the loan using your income, credit history and other factors. Additionally, you’ll need to fill out a Private Education Loan Applicant Self-Certification form through your school’s financial aid office.
- Submit your documentation: You’ll be asked for paperwork proving your identity and financial information; for instance, Social Security card and recent pay stubs. Many private student loan lenders let you apply online and receive a decision quickly.
- Await approval and disbursement: Once you’re approved for a private student loan, you can choose the interest rate type, the repayment plan and other loan terms, and then sign the loan agreement. The lender will contact your school to verify that you’re eligible for the loan amount you requested. Private student loan proceeds are sent directly to the school.
Alternatives to Getting a Private Student Loan
Apply for grants and scholarships. Need-based grants are awarded at the federal, state or college level. As for scholarships, students should start their search locally, and national scholarships are listed on database search websites, including the U.S. News Scholarship Finder.
Consider a cheaper college. Studying for one or two years at a community college before transferring to a four-year college can translate to significant savings. Just be sure that your community college credits will transfer to your university of choice. Also, opting for an in-state public institution may save you tens of thousands on tuition and fees compared to an out-of-state university or a private college.
Ask about a payment plan. Some colleges let you spread out certain costs over monthly payments. These plans usually cover only direct costs, such as tuition and sometimes campus housing and food, and charge an enrollment fee but no interest.
Live at home. Room and board cost over $12,600 on average at in-state, public universities for the 2022-23 school year, according to the Education Department. Determine the cost of your commute to see whether living at home could cut this expense.
Get a part-time job. A part-time job can pay for personal expenses, supplement federal financial aid and help you gain valuable work experience. Some employers may help pay for college, with benefits like tuition assistance or paid internships.
Ask family or friends for support. If someone can help pay for tuition or supplies, accept graciously.
Take a year off. Weigh the total cost of a private student loan against the cost of delaying your education a year and working to save for college, and then decide what suits you best.
Private Student Loan FAQs
How Are Student Loan Interest Rates Determined?
Several factors determine a private student loan interest rate, including the loan amount and repayment length, as well as the borrower’s credit history and debt-to-income ratio. If you have a low credit score or no established credit history, you may be offered a higher interest rate or require a co-signer. Whether you’re pursuing career training, a bachelor’s degree or a master’s degree and whether it is a fixed- or variable-rate student loan also factor in to your private student loan interest rate.
What Credit Score Do You Need for a Private Student Loan?
Most private student loan lenders require a credit score in the mid-600s in order to qualify. If the student doesn’t have a sufficient credit score, the lender may require a creditworthy co-signer who does. Additionally, higher credit scores translate to lower interest rates, and vice versa.
What’s the Difference Between Federal and Private Student Loans?
Private student loans are provided by private lenders and banks, whereas federal student loans are funded by the U.S. government. Private loans aren’t eligible for federally mandated deferment options, forbearance programs and income-driven repayment plans. They also don’t qualify for federal student loan forgiveness and cancellation programs, such as Public Service Loan Forgiveness.
Our Student Loans Methodology
U.S. News selects the Best Loan Companies by evaluating affordability, borrower eligibility criteria and customer service. Those with the highest overall scores are considered the best lenders.
To calculate each score, we use data about the lender and its loan offerings, giving greater weight to factors that matter most to borrowers. The scoring factors for private student loan providers are customer service ratings, fixed APR, variable APR, loan product availability, minimum and maximum loan terms, minimum and maximum loan amounts, minimum FICO score, and online features.
The weight each scoring factor receives is based on a nationwide survey on what borrowers look for in a lender.
To receive a rating, lenders must offer qualifying loans nationwide and have a good reputation within the industry. Read more about our methodology.
Find the Student Loan That’s Right for You
- Looking for private student loans
- Best Private Student Loans
- Refinancing your student loans
- Student Loan Refinancing & Consolidation
- Not using a co-signer
- Student Loans Without a Co-Signer
- Building credit
- Best Student Loans for Bad Credit
- A parent
- Best Parent Student Loans
- An international student
- Best International Student Loans
- Hoping to evaluate multiple lenders at once
- Best Student Loan Marketplace
- Attending medical school
- Best Medical School Loans
- Attending graduate business school
- Best MBA Loans
- Attending graduate school
- Best Student Loans for Graduate School
- Attending law school
- Best Student Loans for Law Schools
- Attending school part time
- Best Part-Time Student Loans
- Seeking a loan with fast co-signer release
- Fastest Co-Signer Release Student Loans





